Nota Bene: If there are terms and acronyms that you use routinely that are missing from this list, please tell us about them so that we may add them to the list.
ACD ... automated call distribution
ACN ... AWIPS Communication Network [AWIPS]
ACU ... Acquisition Control Unit
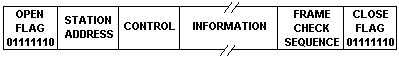
ADCCP Advanced Data Communications Control Procedures: the American
National Standards Institute (ANSI) version of a HDLC protocol that is
used for synchronous transmission of data.
ADAS ... AWOS Data Acquisition System (FAA)
ADDL ... Advanced Development and Demonstration Laboratory
ADP ... automated data processing
AFOS ... Automation of Field Operations and Services
AFPS ... AWIPS Forecast Preparation System
AI ... artificial intelligence
Amplifier: A device used to increase the strength of an analog signal.
AMSU ... advanced microwave sounding unit
Analog A signal, such as voice, that varies in a continuous manner. Signal (Contrast with Digital signal)
ANSI ... American National Standards Institute [AWIPS]
AO ... automated observation
AOMC ... ASOS Operations and Monitoring Center
API ... Application Programmer Interface [AWIPS]
APPN ... Advanced Peer-to-Peer Networking
ARC ... automatic remote collector
ARP ... address resolution protocol
ARP Address Resolution Protocol: The TCP/IP network-layer protocol that
translates an (32 bit) IP address into a (48 bit) physical layer address.
ART The Automatic Radiotheodolite, ART, is a ground-based radio
direction finder that automatically tracks a ballon-borne radiosonde.

ART Description
ART Pictures
ASOS Automated Surface Observing System: NWS system of
weather sensor equipment.

ASOS Description
ASOS Pictures
AS1 ... Application Server 1 [AWIPS]
ASOS Automated Surface Observing System: NWS system of
weather sensor equipment.

ASOS Description
ASOS Pictures
ASOS Comms Diagram
ATM ... asynchronous transfer mode
ATM ... automated teller machine
AUI ... Application User Interface [AWIPS]
AVHRR ... Adveanced Very High Resolution Radiometer
AWIPS Advanced Weather Interactive Processing System: NWS Computer system for
ingesting and displaying weather data for NWS Forecast Offices and River
Forecast Centers.
AWIPS Summary Description
Return to Top of List
Bandwidth - The frequency range between the lowest and highest frequencies
that are passed through a component, circuit, or system with
acceptable attenuation.
Baseband - The frequency band occupied by a single signal in it's original or unmodulated
form.
Baseband - A method of signaling in which only one signal occurs on the tranmission
signaling media at any given point in time.
Baud A unit of signaling speed equal to the number of signal events per second.
Not necessarily the same as bits per second (bps).
bis Meaning second in Latin, this term is used as a suffix to denote a secondary
version of a ITU modem standard.
Bit rate - The speed at which bits are transmitted, usually expressed in
bits-per-second. Not neccessarily the same as baud rate.
BMP ... bitmap (type of electronic image)
bootp - Network protocol which allows systems to get configuration/boot information
from some other more authoritative or more intelligent system typically residing
on the local LAN.
bps (bits per second) A measure of the information transfer rate of a channel.
BPI ... bits per inch
BPS ... bits per second
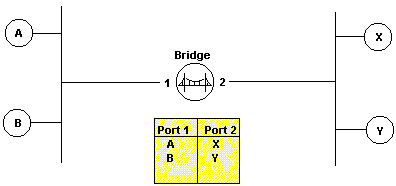
Bridge A device that expands a local area network by forwarding packets based
on the (48 bit) physical address. In OSI terminology, a bridge operates at
the Data Link Layer (layer 2).
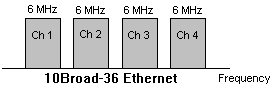
Broadband - A method of signaling in which multiple signals share the bandwidth
of the transmission by the subdivision of the bandwidth into
channels based on frequency.
Browser - A program that is used as a GUI (Graphical User Interface) for retrieving and
viewing html documents (Web Pages) from the World-Wide-Web (Internet). Documents
are transferred using the http protocol.
Return to Top of List
CAD ... computer-aided design
CADD ... computer-aided design and drafting
CAI ... computer-aided instruction
carrier - A signal suitable for modulation by another signal containing information
to be transmitted. The carrier is usually a sine wave for analog systems.
CCITT - Consultative Committee for International Telephone and Telegraph
CD ... compact disk
CD-ROM ... compact disk, read-only memory
cell A 53-byte-long transmission unit used by ATM. Each cell has a 5-byte header
and 48-byte payload.
channel, voice grade - A channel, generally with a frequency range of about 300 to
400 Hz, suitable for transmission of speech or data in
analog form. Data transmission rates of 9600 Bps can be
achived by modulation techniques that produce a baud rate
of 2400.
CIR ... committesysinformation rate
client - A workstation/program which requests a network service from another system.
Comms A device that connects many terminals to a LAN through one
Server network connection. The terminal may be remoted through a modem.
This is also sometimes called a terminal server.
Pictures of Terminal/Comm Server
committesysinformation rate - The minimum operating rate supported by a frame-relay service.
connection-oriented - A type of communication in which a connection must be established
between the sender and receiver before transmission occurs.
contention - The facility provided by dial networks or a port selector that allows
multiple terminals to compete on a first-come-first-served basis for
a smaller number of computer ports
COTS ... Commercial Off-the-Shelf (software and hardware) [AWIPS]
CP : COMMUNICATIONS PROCESSOR
View info on AWIPS CP
CRON - A UNIX utility that can automatically start jobs/programs at
specified times, dates, day-of-week, etc...
CPU ... central processing unit
CRS = Console Replacement System for NOAA Weather Radio. CRS Description CRS Pictures
CRT ... cathode ray tube
CSMA/CD Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detect: a local area network
access technique in which multiple stations connected to the same
channel are able to sense transmission activity on the channel and to
defer the initiation of transmission while the channel is active. In addition
the stations are able to detect the interference caused by simultaneous
transmissions by 2 or more stations (collisions) and to retransmit colliding
messages in an orderly manner.
CSU Channel Service Unit terminates the high-speed circuit, performs signal
regeneration, monitors for bipolar violations, and performs remote
loopback testing. A CSU can be used on either a T1 or a fractional T1.
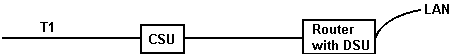
View NEXRAD CSU Info.
View DSU/CSU pic.
CW ... continuous wave
Return to Top of List
daemon A UNIX program that runs as a background process (similiar to a DOS TSR)
DAT ... digital audio tape
DATACOL ... software system supporting RFC gateway functions
db ... decibel
DBMS ... Data Base Management System
DC ... direct current
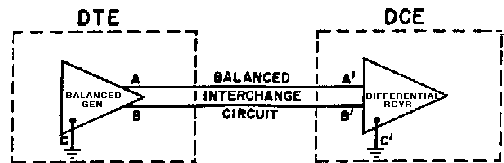
DCE Data Communications Equipment: The equipment that provides the
functions required to establish, maintain and terminate a
connection, and that provides the signal conversion required
for communication between data terminal equipment and telephone
line or data circuit.
DSX-1 Actual data rate achieved on a DS-1 (T1) minus the 8k of framing bits/sec
that is equal to 1.536Mbps. Term is used in 88D 520 manual.
DCP ... data collection platform (satellite)
DCP ... data collection package (ASOS)
DDT ... design, development and test
DFD ... Data Flow Diagram [AWIPS]
demodulation - The process of recovering data from a modulated carrier wave.
The reverse of modulation.
DIFAX ... digital facsimile
DNS Domain Name System: The distributed name and address mechanism
used in the Internet.
DOS ... disk operating system
DSU Digital Service Unit converts incoming digital data into the bipolar format
for transmission over a T1 or fractional T1. Fractional T1 can operate at
speeds up to 56Kbps or 64kbps clear channel.
View DSU/CSU pic.
DSU/CSU With divestment of the Bell system the DSU and CSU functions may be
combined in one unit.
DS-1 Digital signaling rate of 1.544Mbps used on T1
DTE Data Terminal Equipment. A computer that provides data in the form of
digital signals as it's output.
DS1 ... Data Server 1 [AWIPS]
Return to Top of List
Eb/No ... Energy per Bit over Noise density associated with the SBN operation [AWIPS]
Ethernet A 10Mbps bus standard for LANs using the IEEE 802.3 frame and
CSMA/CD but address and control slightly differ from 802.3. Ethernet and
802.3 require different software drivers (See OSI model).
Download ETHERNET cbi course
Return to Top of List
FDDI Fiber Distribution Data Interface: a high-speed (100Mbps) LAN standard.
The underlying medium is fiber optics, and the typical topology consists of
dual-attached, counter-rotating rings. IEEE 802.8 is the standard for
FDDI.
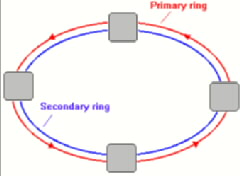
FDDI pictures
Download FDDI cbi course
FDM Frequency Division Multiplexer: A device that divides the available
transmission frequency range into narrower bands, each of which is
used for a separate channel.
FEP ... front-end processor
FIPS ... Federal Information Processing Standard
Firewall - Equipment and/or software configured to provide enhanced security between networks.
Flow-control: The orderly regulation of the flow of data by the use of special characters (inband signaling) or control signals at the RS232 interface (outband signaling)
FM ... frequency modulation
FORTRAN ... Formula Translation Language (programming language) [AWIPS]
Frame-relay : A packet switched service that does not provide for error detection
and correction, resulting in minimal routing delays.
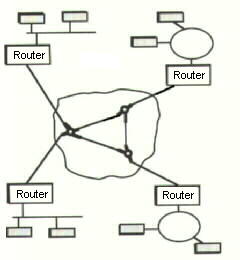
Frame_relay Circuit components diagram
FTP File Transfer Protocol: A TCP/IP protocol that lets a user on one computer
access and transfer files to and from another computer over a network.
FTS ... Federal Telephone System
Full Duplex - Refers to a communications system or equipment capable of
simultaneous two-way communication.
Return to Top of List
Gateway In the TCP/IP world a router is referred to as a gateway because it is the
gateway to wide area networking. For everybody else a gateway is the
device that allows a network to access the facilities of another network.
gated A UNIX routing program that supports multiple routing protocols
GIF ... graphics interface format (type of electronic image)
GMT ... Greenwich mean time
GOES ... Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite
GOES-NEXT ... Next Generation Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite
GOSIP ... Government Open Systems Interconnection Profile
GTA ... ground to air
GTE ... General Telephone Spacenet [AWIPS]
GTS ... Global Telecommunication System
GUI ... Graphical User Interface [AWIPS]
Return to Top of List
Half-duplex - Refers to a communications system or equipment capable of communication
in both directions, but in only one direction at a time.
Handshaking - Exchange of predetermined codes and signals between two data terminals
to establish a connection.
HCI (HI) ... Human Computer Interface [AWIPS]
HCL ... Hydrologic Command Language [AWIPS]
HDLC High-level Data Link Control. ITU standard for bit-oriented, data-link
control protocol, with error correction that is used for synchronous data
transmission.

HF ... high frequency
HIPS ... High Resolution Picture Transmission (HRPT) Image Processing System
HIRS ... high-resolution infrared sounder
HIRS-2 ... high-resolution infrared sounder, version 2
HIRS-3 ... high-resolution infrared sounder, version 3
HMI ... Human/Machine Interface [AWIPS]
Host Term used to refer to a TCP/IP workstation.
HP-UX A version of the UNIX operating system that is used on Hewlett Packard systems.
HRDI ... high-resolution Doppler imager
HRIR ... high-resolution infrared radiometer
HRPT ... high-resolution picture transmission
HSP ... hard-wired signal processor
HTTP Hyper-Text Transfer Protocol - a protocol used to transfer html documents over
the Internet/Intranet. The protocol is invoked through the use of a client
program called a browser.
HTML Hyper-text Markup Language a computer coding language used to create text/graphics
documents suitable for viewing via a browser(see HTTP).
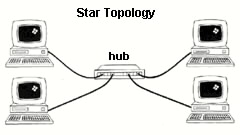
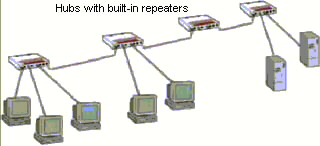
hub A piece of equipment used in Ethernet/10BaseT LANs to connect multiple
workstations or devices together logically and physically to a single
location. The hub has multiple RJ-45 connectors. Internally it has a
single bus.

Pocket-Hub Pictures
Hz ... hert
Return to Top of List
IEEE - Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (U.S.)
SUMMARY CHART of IEEE 802 Standards
IEEE 802.2 A data link layer control (LLC) standard used with 802.3, 802.4, 802.5 and
802.8
IEEE 802.3 A physical layer standard specifying a linear (bus) LAN using CSMA/CD
access method. Ethernet is a similar standard but not an IEEE
encapsulation. Usually 10Mbps.
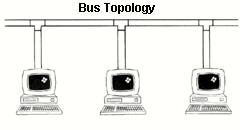
IEEE 802.4 A physical layer standard specifying a linear (bus) LAN using token-
passing access method. Usually 10Mbps.
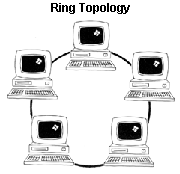
IEEE 802.5 A physical layer standard specifying a ring topology LAN using token-
passing access method. IBM's token ring follows this standard. May
operate at 4Mbps or 16Mbps.
IEEE 802.8 A specification for a (FDDI) Fiber Distributed Data Interface LAN to
connect to a fiber optic transmission system using the token-passing
access method.

IFPS - Interactive Forecast Preparation System (used in AWIPS).
Forecasters use IFPS to create a digital database of predicted weather elements
from which a suite of text, tabular, and image forecast products are automatically
created and formatted.
View IFPS Training
Informix - Commercial (Relational) Database Management System (RDBMS) used in AWIPS.
Download Introductory NWSTC Informix O.V. materials
View online NWSTC DB/Informix concepts overview doc.
Informix Web-Site
Interface - A shared boundary defined by common physical interconnection characteristics,
signal characteristics, and meanings of interchanged signals.
Internet - A network term for that is most commonly used to describe a collection of networks
interconnected with routers.
Intranet - An Internal WAN not directly connected to the Internet.
IP - Internet Protocol is the network layer protocol for a connectionless, best-
effort packet delivery service. Is used to route packets through a switched
network.
CLICK HERE for more information on IP addressing
CLICK HERE for online instruction on IP addressing
IPX/SPX - a protocol stack used in Novell LANs
IR ... Infrared
IS ... Information systems
ISDN Integrated Services Digital Network: A communication offering designed to
provide a universal digital network that will enable the integration of
voice and data on a common telephone facility.
ISO International Standard organization. Volunteer organization involved
with developing standards for computers and networks.
IT ... Information technology
ITU An International standards committee. Formally known as CCITT.
Return to Top of List
JCL ... job control language
jet-direct - a NIC(network interface card) licensed to Hewlett Packard specifically
designed for connecting peripherals such as printers/plotters directly
to a LAN.
jitter - a tendency toward lack of synchronization caused by mechanical or
electrical changes.
Return to Top of List
kb ... kilobit
kbps ... kilo bits per second [AWIPS]
kB ... kilobyte
kernel A term used in operating systems to mean the core O/S. The kernel is responsible
for the low-level functions such as hardware management.
kHz ... kilohertz
Return to Top of List
LAN: (see Local Area Network)
LAPM Link Access Protocol for Modems. A ITU link layer (HDLC ) protocol built-in
to modems for V.42 error correction.
LAPB Link Access Protocol Balanced. A HDLC protocol part of the X.25
standard for access to a packet switching network.
View info. on LAPB use in NEXRAD
LAPD Link Access Protocol for D-channel. Originally developed as an HDLC
protocol for ISDN and is also used in frame relay networks.
LAPS ... Local Analysis and Prediction System
LARC ... limited automated remote collector (replaced DARDC)
LBC ... laser beam ceilometer
LDAD : Local Data Acquisition and Dissemination (external interface to AWIPS) View info on AWIPS LDAD View LDAD diagrams/add'l info.
LDS ... Lightning Detection System
LED ... light-emitting diode
LEDWI ... light-emitting diode weather indicator [ASOS]
Linux - a derivative of the UNIX operating system which runs on Intel and other PC platforms.
Local Area Network : A communications network that is restricted to a small geographic
area, usually within a building or on a campus, and that has
cabling normally installed or controlled by the organization that
operates the network.
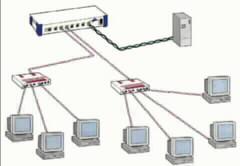
View more detailed LAN definition/info.
Local loop : The pair of wires between a phone customer terminal and the central office.
Loopback test : A test of a communications link performed by connecting the
equipment output of one unit to the equipment input of
the other unit and testing the quality of the received
signal.
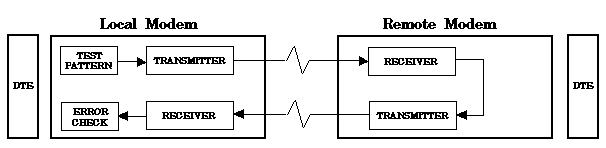
Return to Top of List
mbps ... mega bits per second
MHz ... megahertz
MIME ... multipurpose Internet mail extension
MIS ... Management Information System
MNP An acronym for the Microcom Inc. protocols called Micro Networking
Protocol. MNP is divided into 10 classes. Two MNP modems negotiate to
the highest mutually supported class. MNP classes 2-4 error correction
and MNP 5 data compression has been licensed to many modem
manufacturers.
Modem - MOdulator/DEModulator: A type of DCE that at the transmitting end converts
digital data to an analog signal for transmission on telephone circuits.
A modem at the receiving end converts the analog signal to digital form.
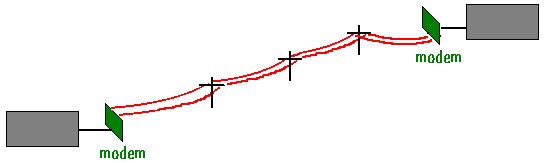
View Modem Circuit diagrams
Download MODEMS cbi course
modulation - The process of varying some characteristics of the carrier wave in
accordance with the instantaneous value or samples of the intelligence
to be transmitted. Amplitude, frequency, and phase are the characteristics
commonly varied.
MPEG ... Movie Picture Expert Group
Multiplex - To interleave or simultaneously transmit two or more messages on a single
channel.
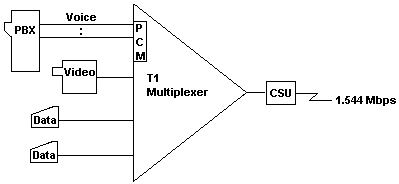
Return to Top of List
NCF Network Control Facility: NWS & PRC managed help desk facility for AWIPS.
NCF tel# = 301-713-1284
NCF Web-Site
NESDIS : National Environmental Satellite Data and Information Service
NetBeui - a protocol stack used in native MicroSoft LANs
NetCDF : NETwork Common Data Form : data storage and retrieval software
interface and file structure used in AWIPS. NetCDF provides
portable, self-describing data files particularly suitable to
uniform multi-dimensional data sets.
Network Interface Card - a computer board/card that is used to connect the computer
to the local network.

View card and connector pics ansysinfo
NEXRAD: NEXt generation RADar: The NEXRAD system is an interconnected
system of Doppler meteorological radars (WSR-88Ds) destined
for approximately 175 sites throughout the continental United
States, in portions of Alaska, Hawaii and Puerto Rico,
and at selected overseas military bases.

NEXRAD Description
NEXRAD Pictures
NFS Network File System: is software that lets a client program running on one
computer use a networked server computer's disk drive as if it were a
local disk. It is a Sun Microsystems distribution that has been licensed to
hundreds of products.
NIC Network Interface Card (see Network Interface Card)
NIS Network Information Service: Formally called "yellow pages" this
software allows configuration files such as passwd, hosts, etc...
to be managed in a single location and sharable across the LAN.
node = a piece of equipment (computer/Host, device ...) at a location on a
network.
Noise - Random electrical signals, introduced by circuit components or natural
disturbances, that tend to generate errors in transmission.
Novell
Netware Family of networking operating systems based on the SPX/IPX protocols
for the transport-layer.
Null Modem
View null modem cable/pin config.
NWSTG : National Weather Service Telecommunications Gateway
Return to Top of List
ORDA ... open radar data acquisition
ORPG ... open radar product generator
OS ... Operating system
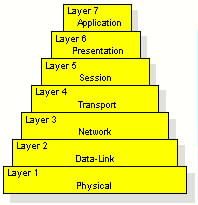
OSI OPEN SYSTEMS INTERCONNECTION. A 7-layer network protocol model designed
by the ISO committees intended to be the international standard computer
network architecture.

View more detailesysinformation on the OSI model
OSPF Open Shortest Path First: A gateway protocol that utilizies
actual time vectors to determine the best routing for
messages (as opposed to RIP which uses hops).
Return to Top of List
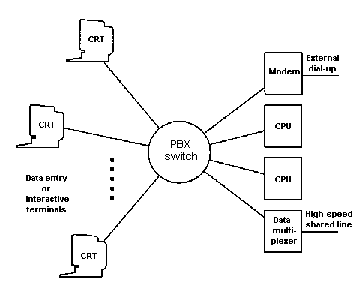
PBX Private Branch eXchange: Telephone switching equipment dedicated to one
customer and connected to the public switched network.
PPP Point-to-Point Protocol: The standard serial protocol for communication to
the Internet. PPP has an HDLC error correction that SLIP was lacking. PPP
can be used for both synchronous and asynchronous data.
Polling The individual selection of multiple terminals by a controller to allow
transmission of traffic to and from all terminals on a multidrop line
in an orderly manner.
Port A logical pointer to an TCP/IP application such Telnet, FTP etc.
POSIX ... Portable Operating System Interface [AWIPS]
PPP ... point-to-point protocol
Print Server - A computer or device which serves as the interface and control
mechanism to a network accessible printer.
Protocol A formal description of message formats and rules that equipment must
follow to exchange those messages. A group of protocols interfacing
together, such as in a LAN, are referred to as a stack.
(See OSI layered architecture)
Protocal Analyzer - A device that decodes a bit stream being monitored into
characters that represent the format ansysinformation content
of a transmitted protocol
PTM ... point to multipoint
PTP ... point to point
PVC Permanent Virtual Circuit: A logical connection between endpoints in a
network that remains in place until the network administrator tears it
down.
Return to Top of List
No terms defined.
Return to Top of List
RADID ... radar information display
RAM ... random access memory
RARP Reverse Address Resolution Protocol. The Internet protocol that finds the
IP address to match a known physical address. It is primarily used by
diskless workstations.
Repeater In 802 Ethernet a repeater is used to extend the segment by simply
regenerating the electrical signal. The electrical signal is considered the
physical or OSI layer 1.
RCM ... radar coded message
RDA ... radar data acquisition [WSR-88D]
RDBMS ... Relational database management system [AWIPS]
RF ... radio frequency
RFI ... radio frequency interference
RJE ... remote job entry
RIP Routing Information Protocol: An Interior routing protocol supplied with
UNIX and most routers. RIP is used to update routing tables in a network
that uses routers. (OSPF is a newer protocol being widely used in routers).
ROSA ... Remote Observation System Automation
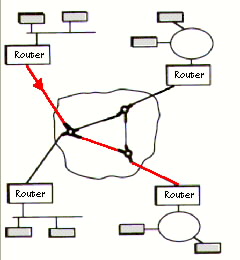
Router A device that forwards traffic based on network-layer or the IP address in
TCP/IP. These are usually smart devices that can provide alternate
routes if one is down.
Router pictures
CLICK HERE for online instruction on routing & gateways/routers
Routing A network-layer function whereby a network device determines where to
send packets across the network based on the network-layer address.
RPG ... remote product generator
RPG ... radar product generator [WSR-88D]
RPGOP ... radar product generator operational position [WSR-88D]
RPM ... revolutions per minute
RS-232 An interface standard between the Data Terminal Equipment (Com port)
and the Data Communications Equipment (modem).
RS-422A Standard for data signaling, using 2-wire balanced transmission.
RS-449 An interface standard between DTE and DCE using balanced
transmission of data. Uses a DB-37 connector and may have a DB-9
connector for secondary channel.

RS-530 An interface standard that uses balanced data transmission and DB25
connector.
Return to Top of List
SBN ... Satellite Broadcast Network
SCSI ... Small Computer Systems Interface
Serial transmission - A method of information transfer in which the bits that
compose a character are sent in sequence one at a time.
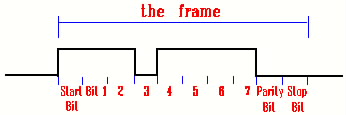
SLIP Serial Link Interface Protocol: A non-standard network layer protocol that
allows for point-to-point communications via TCP/IP across a serial line.
Lacks the error correction capabilities of PPP but is satisfactory for direct
computer-to-computer links.
SMTP Simple Mail Transfer Protocol: An applications layer protocol used for
sending and receiving mail. It also provides specifications for functional
third party E-mail system (CC-MAIL) interaction and control.
SNMP ... Simple Network Management Protocol
SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol: A protocol used by network
components, such as bridges, routers, and other intelligent network
management devices, to exchange network-management information.
SPX/IPX SPX is the transport layer protocol developed by Novell. SPX is not used
much even by Novell. The IPX protocol has proven to be fast and
efficient, particularly with the relatively small data packets---in the 512 byte
range--- usually requested by DOS and Windows applications. IPX is
bundled in most network operating systems including Windows, Windows NT,
LANtastic, and Power Lan. However IPX's small packets aren't
desirable on wide area networks, where TCP/IP is preferred, but IPX
packets are more effective on a Local Area Network.
SQL ... structured query language
Socket A port number combined with IP address that identifies a particular
Address logical connection in use by an application system.
subnet A portion of a network that shares a network address with other subnets but is
distinguised by a unique subnet number. A subnet is to a network as a network is
to an internet.
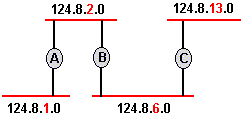
Subnet address / number - a part of the IP address which designates the locally administered
subnet
subnet mask - a number which is used in a network (i.e. Internet) used to interpret which
IP address bits are used for network, subnetwork (see subnet above),
and host identification.
CLICK HERE for online instruction on subnetting
swap - information normally utilized in computer memory that has been written
to temporary disk space because of limited memory.
Switch Switching Hub: a multiport Ethernet device designed to increase network
performance by allowing only essential traffic on the attached individual
Ethernet segments. Packets are filtered or forwarded based upon their
source and destination physical addresses. The distinction between
bridges and switches has become blurred. Switch is now used to refer to
a multiport device that operates at Ethernet wirespeed.
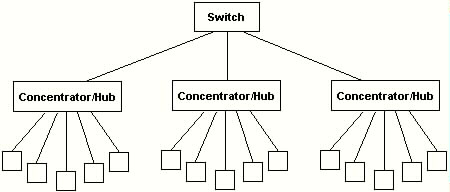
Switch pictures
Synchronous transmission - Transmission in which the sending and receiving instruments
are operating continuously at substantially the same
frequency and in which the desired phase relationship
can be maintained by means of correction.

Return to Top of List
T1 Term for digital carrier used to transmit DS-1 (1.544Mbps) formatted data.
Term often used for DS-1 signaling speed.
TCP An Internet transport protocol to provide reliable, connection-oriented, full-
duplex bit streams.
TCP/IP Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet Protocol: an internet transport
protocol providing reliable, connection-oriented, full-duplex bit streams
with IP's ability to route packets through a WAN.
CLICK HERE for online instruction on TCP/IP
TCP/IP Or TCP/IP stack (See OSI layers): A group of protocols developed for internetworking
Suite systems with differing computing platforms ( i.e. IBMs with DECs with PCs
with Unix etcetera ) over a LAN or a WAN. Also used on the Internet.
Includes IP, ICMP, TCP, UDP, FTP, Telnet, SMTP, SNMP, TFTP
TDM Time Division Multiplexer: A device that allows the transmission of
two or more independent data channels on a single high-speed circuit
by interleaving the data from each channel on the circuit by time.

Telnet The virtual terminal protocol that lets users on one host access another
host and work as terminal users of the remote host.
Terminal - A device that connects many terminals to a LAN through one network
Server connection. The terminal may be remoted through a modem.
Pictures of Terminal/Comm Server
TFTP Trivial File Transfer Protocol: A TCP/IP protocol that lets a user on one computer
access and transfer files to and from another computer over a network. For TFTP as
opposed to FTP this is usually done with much less user intervention/overhead and
can be done automatically without user/password access.
TIFF ... taged image file format
Topology - The 'shape' a network takes, such as a star (with a centralized hub) or
a bus (equipment strung on one open-ended cable serially from end to end),
a ring (circular closed-ended cable(s), etcetera...

[AWIPS]
Return to Top of List
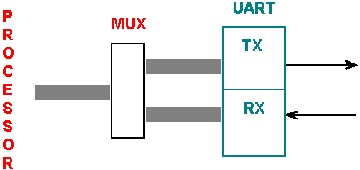
UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter: A device that performs
asynchronous communication functions by converting parallel digital
output from a DTE into serial bit transmission and vice versa.
UDP User Datagram Protocol: an Internet transport protocol that exchanges
datagrams without acknowledgments or guaranteed delivery.
UDP ... User Datagram Protocol [AWIPS]
UHF ... ultra high frequency
UNIX A powerful networkable multi-user operating system. In the NWS UNIX is used in
AWIPS, and CRS. Currently there is no single UNIX standard but rather several
variants including AIX, HP-UX, Linux, Solaris, SCO, UNIXWare, etcetera...
UNIX reference pages
NWSTC UNIX courses (Intro, SA, SysSpt, NetSec, INFORMIX)
UNIXWare - a verion of UNIX formally distributed by Novell but now owned by SCO. UNIXware is
used in CRS
UPS ... uninterruptible power supply
URL ... uniform resource locator (Internet address)
Return to Top of List
V.22bis ITU standard for 2400 bps, full duplex, transmission over a switched
telephone network.
V.24 ITU standard for DTE to DCE interface. Nearly equivalent to RS-232.
V.25 ITU standard for an automatic call unit, often internal to the modem, for
dialing from an asynchronous DTE port only.
V.25bis ITU standard for an automatic call unit, often internal to the modem, for
dialing from an asynchronous or synchronous DTE port.
V.32 ITU standard for 9.6 Kbps, full duplex, transmission over a switched
telephone network.
V.32bis ITU standard for 14.4 Kbps, full duplex, transmission over a switched
telephone network.
V.34 ITU standard for 28.8 Kbps, full duplex, transmission over a switched
telephone network.
V.35 ITU DTE-DCE interface standard that is no longer published but still
widely used. The term has come to refer to a high speed,low capacitance,
shielded interface with a 34-pin winchester connector. V.35 interface is
common on bridges, routers and DSU/CSUs.
V.42 ITU standard for error correction at the modem for asynchronous data
only. Also the mechanism for negotiating: (1) LAPM (HDLC) or (2) MNP 2-
4 error correction.
V.42bis ITU standard for data compression at the modem for asynchronous data
only. V.42 error correction must be established first and then V.42bis will
negotiate for V.42bis (Lempel-Ziv) or MNP 5 data compression.
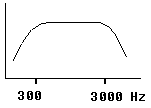
Voice Has been established with a bandwidth of 0 hz to 4000 hz, however the
channel effective bandwidth is 300 hz to 3000 hz at -3dB points after phone
company filtering and the electrical characteristics of the local loop.
VHF ... very high frequency
Return to Top of List
WAN Wide Area Network: A network that covers a wide geographic area.
WSR ... weather surveillance radar
WSR-57 ... weather surveillance radar - 1957
WSR-74C ... weather surveillance radar - 1974
WSR-88D ... Doppler weather surveillance radar
See NEXRADReturn to Top of List
X-Terminal - a graphical (X-Windows) display which must get it's configuration
information from another device.
XMODEM - A half-duplex file transfer protocol limited to transmitting one file at
a time.
Return to Top of List
YMODEM - A half-duplex file transfer protocol that supports the transfer
of multiple files.
Return to Top of List
ZMODEM - A full-duplex file transfer protocol that supports the transfer of multiple
files and enables a previously interrupted transmission to be resumed at the
point of interruption.
Zyplex Comms/terminal Server used in AWIPS.
Zyplex pictures
10Base2 : An IEEE standard for thin coax (ThinNet) Ethernet network.
(10mps - Baseband transmission - 200 meters)

10BaseT : An IEEE 802.3 standard for unsheilded Twisted-pair Ethernet network.
(10mps - Baseband transmission)

Return to Top of List
Return to NWSTC Home Page
![]() NWSTC - Updated 02-08-05
NWSTC - Updated 02-08-05