
| {column0} |
| {column0} |
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a space-based radio-navigation system consisting of a constellation of satellites and a network of ground stations used for monitoring and control.
- Background
- Impacts
- Watch A Video
 GPS is operated and maintained by the Department of Defense (DoD). Global Positioning Systems are being used for ever more precise applications, including mapping of coastlines, surveying for highway construction, landing airplanes, and oil drilling.
GPS is operated and maintained by the Department of Defense (DoD). Global Positioning Systems are being used for ever more precise applications, including mapping of coastlines, surveying for highway construction, landing airplanes, and oil drilling.
When at least four satellites are in view, a user can obtain an accurate, three-dimensional position. At times when more than four satellites are visible from one location, the navigator enjoys an even greater level of confidence in the computed position.
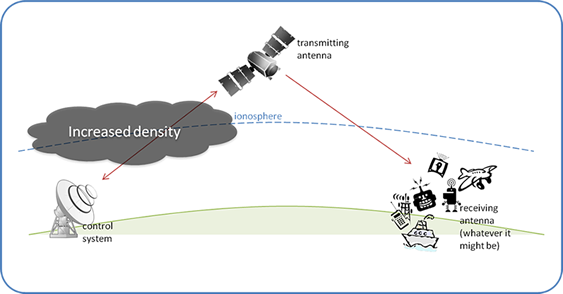
Unlike the low-frequency radio transmissions used by terrestrial systems, GPS uses radio signals that pass through the ionosphere. GPS signals are therefore affected when solar activity causes sudden variations in the density of the ionosphere.
Once you have viewed all of the tabs, click here to view your normal page navigation.