
| {column0} |
| {column0} |
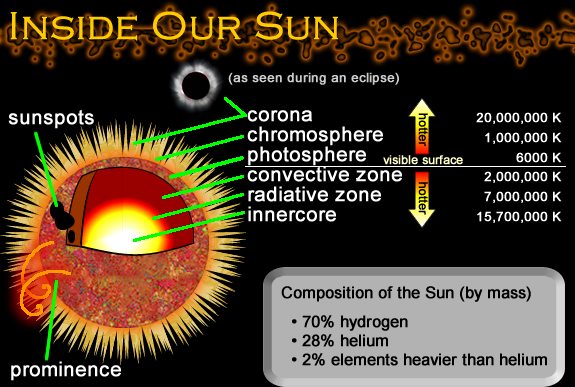
When we forecast space weather, we are really looking at the conditions in space that affect the Earth and its technological systems.
As our country, and mankind in general, continues to become more and more dependent on technology, the effects of space weather will continue to increase.
Nearly all of our space weather starts at the Sun.
The Solar Cycle
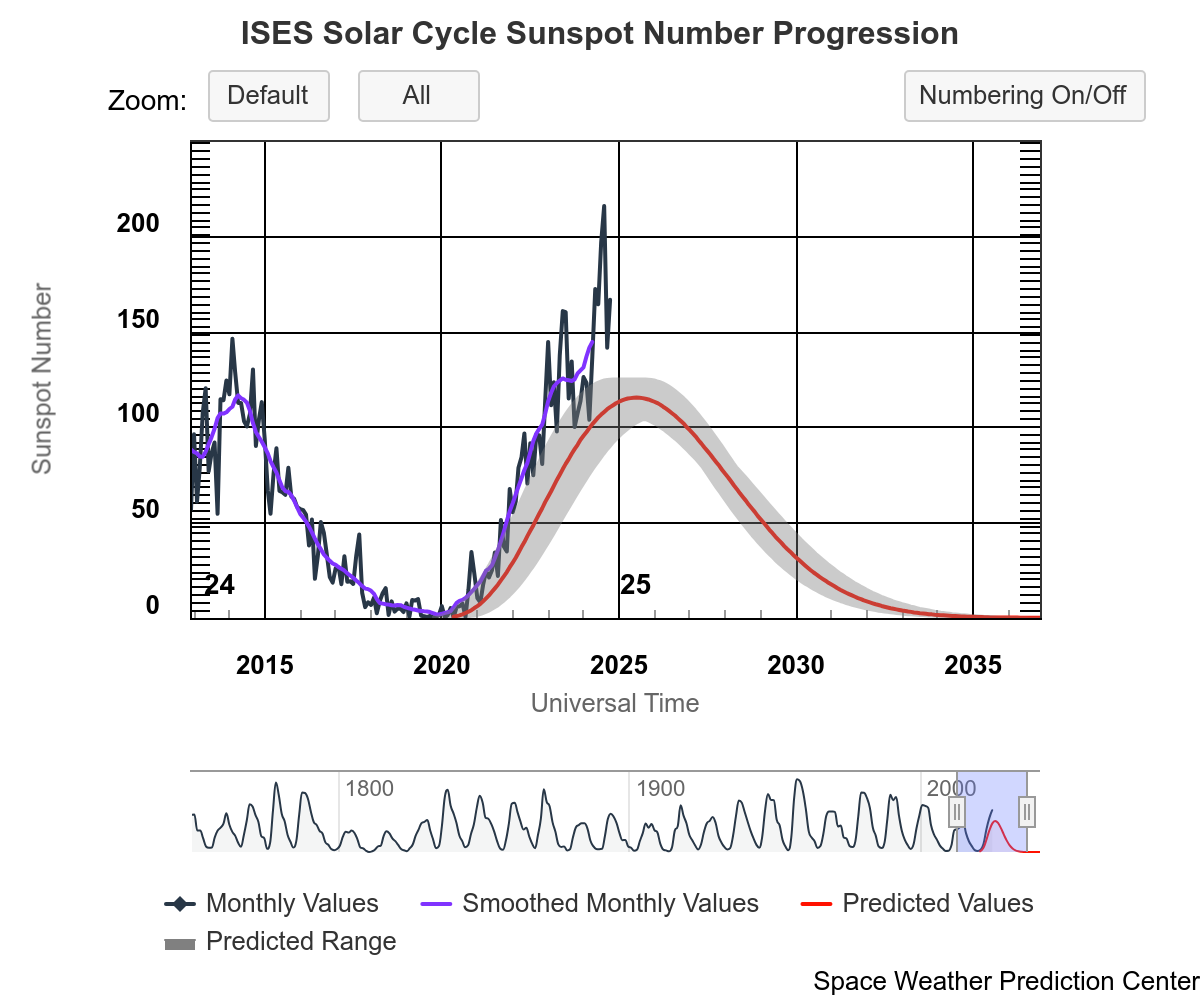 The solar magnetic field changes on an 11 year cycle. Every solar cycle, the number of sunspots, flares, and solar storms increases to a peak, which is known as the solar maximum.
The solar magnetic field changes on an 11 year cycle. Every solar cycle, the number of sunspots, flares, and solar storms increases to a peak, which is known as the solar maximum.
Then, after a few years of high activity, the Sun will ramp down to a few years of low activity, known as the solar minimum. This pattern is called the "sunspot cycle", the "solar cycle", or the "activity cycle".
[This information is courtesy of SOHO. The image on the right is from SWPC's Solar Cycle Progression page.]
Solar Storm
Nearly all of our space weather propagates from the Sun in one of three forms; electromagnetic radiation, energetic particle radiation and geomagnetic storms. The chart below should refresh your memory on these events.
| Phenomena |  |
 |
 |
Definition/ description |
... a cloud of plasma, or superheated gas, being blasted away from the Sun at anywhere from roughly 1 to 5 million miles per hour |
...eruptions of charged particles, i.e. protons and electrons, from the Sun which predominately follow the prevailing interplanetary magnetic fields (the pinwheel effect). |
… an eruption of radio emissions from the Sun which appears to be a very bright spot and a gaseous surface eruption which occur abruptly and with little warning. |
Timing from |
17-96 hours |
10 minutes - several hours |
8 minutes |
| Agents | Energetic Charged Particles from the solar wind, coronal mass ejections and coronal holes. | Solar Flares and CMEs | Solar Flares and radio bursts |
Impact to Earth’s Atmosphere |
The impact of the material hurled at Earth impacts and distorts the Earth’s magnetosphere. This distortion creates magnetic field fluctuations that create induced currents in the atmosphere and on the ground. |
The charged particles interact with the atmosphere to help increase the density of the ionosphere. |
The impacts of these radiowaves can heat the Earth’s atmosphere and create a layer known as the ionosphere. |
Impacts to Human Life |
The induced currents can cause issues with long power lines and pipelines, while the particles themselves can damage satellites. |
Risks include blackout of high frequency radio communications near the polar regions, and possible increase in radiation risks to astronauts and high altitude polar routes. Satellites may experience bit flips that may result in memory loss as well as cause spurious signals to send false commands. |
Impacts include degradation or impairment of GPS & HF Communications. |
The Space Weather Prediction Center (SWPC) is our nation’s official civilian source of space weather alerts and warnings. The SWPC’s mission is to “Safeguard Society with Actionable Space Weather Information to meet the evolving needs of the nation.”
Your customers will most likely be average every-day citizens who have interests, read an article, saw a news story, or otherwise recently learned about Space Weather phenomena.
Congratulations. You have reached the end of Lesson 1.